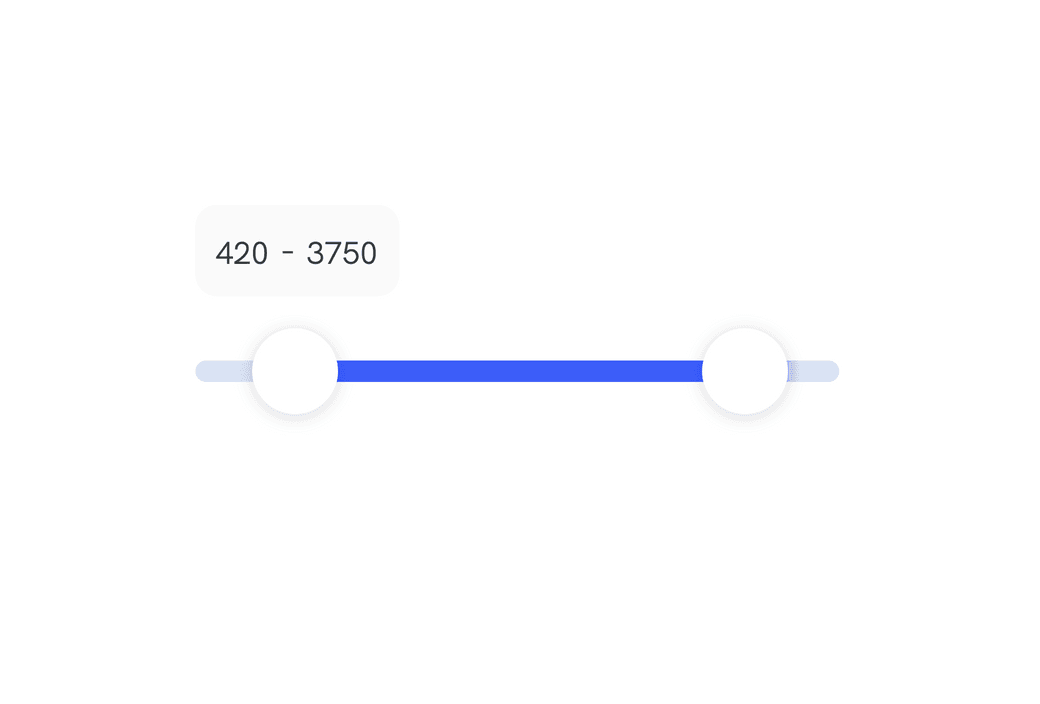
How to: Dual range slider in React with Framer Motion
We will learn how to implement a range slider with two thumbs with Framer Motion
In this article I'll show how we achieved to create a dual range slider from scratch in React with Framer Motion.
Tech stack
This component was built at Level30Wizards, the Tech Stack we used to achieve this is:
- React for markup, templating, routing, etc.
- Framer Motion for animation
- EmotionCSS to write normal CSS, nest selectors and componentize styles
Goal
We want to create a slider with two thumbs that allow us to pick a range between two values. The slider should add the values to hidden inputs for easy access when submitting forms.
Markup
1<div>2 // The are the inputs that will capture the values of the slider.3 <input4 type="hidden"5 name={'price-min'}6 value={(max / (trackWidthInPx / knobX)).toFixed(0)}7 />8 <input9 type="hidden"10 name={'price-max'}11 value={(max / (trackWidthInPx / knobXSecond)).toFixed(0)}12 />13 // A title or label14 <p15 style={{16 textAlign: 'left',17 fontWeight: 'bold',18 margin: '.5rem 0',19 }}20 >21 {label}22 </p>23 // These are small amount labels that show the selected value of both thumbs.24 <AmountLabels>25 <small26 style={{27 marginBottom: '0.25rem',28 marginRight: '0.25rem',29 }}30 >31 {/* If knobX isnt 0 or lower we set the textvalue on the track */}32 {knobX > 033 ? Math.ceil(34 parseInt((max / (trackWidthInPx / knobX)).toFixed(0), 10) / 535 ) * 536 : t('filters.priceRange.noMin')}37 </small>38 {'-'}39 <small40 style={{41 marginLeft: '0.25rem',42 marginBottom: '0.25rem',43 }}44 >45 {/* We set the text value for knobXSecond */}46 {Math.ceil(47 parseInt((max / (trackWidthInPx / knobXSecond)).toFixed(0), 10) / 548 ) * 5}49 </small>50 </AmountLabels>51 // This is the "rail/track" where the thumbs will slide on.52 <motion.div css={Track} ref={constraintsRef}>53 // The first thumb (or knob)54 <motion.div55 css={Knob}56 drag="x"57 initial={{58 x: knobX,59 }}60 dragMomentum={false}61 // When you stop dragging we update the AmountLabel value62 onDragEnd={() => {63 const minPrice = Number(getValueOfKnob(knobX));64 setSliderMin(minPrice);65 }}66 // While you're dragging we update the knobX state67 onDrag={(event, info) => {68 // Check if the point where you slide is bigger than second knob...69 // knobSeparatorLength is a magic value for 2rem size of the knobs. This will influence the bounds of the knobs70 const newValue =71 info.point.x > knobXSecond - knobSeparatorLength72 ? knobXSecond - knobSeparatorLength73 : info.point.x;74 //Math.ceil(N / 5) * 5; rounds to nearest 575 updateKnobX(newValue < 0 ? 0 : Math.ceil(newValue / 5) * 5);76 }}77 // Cant be dragged further than...78 dragConstraints={{79 left: 0,80 right: knobXSecond - knobSeparatorLength,81 }}82 />83 // The second thumb (or knob)84 <motion.div85 css={Knob}86 drag="x"87 initial={{88 x: knobXSecond,89 }}90 dragMomentum={false}91 onDragEnd={() => {92 const maxPrice = Number(getValueOfKnob(knobXSecond));93 setSliderMax(maxPrice);94 }}95 onDrag={(event, info) => {96 // Check if the point where you slide isn't smaller than first knob and not bigger than bounds...97 const newValue =98 info.point.x > trackWidthInPx99 ? trackWidthInPx100 : info.point.x < knobX + knobSeparatorLength101 ? knobX + knobSeparatorLength102 : info.point.x;103 updateKnobXSecond(Math.ceil(newValue / 5) * 5);104 }}105 dragConstraints={{106 left: knobX + knobSeparatorLength,107 right: trackWidthInPx,108 }}109 />110 </motion.div>111</div>
CSS
When you use EmotionCSS, you can use props to determine styling.
An example of this can see seen in the CSS block of the Track. There we calculate a linear-gradient based on the position of the thumbs.
1const Knob = styled.div`2 ${({ knobSize }: any) => css`3width: ${knobSize}rem;4height: ${knobSize}rem;5border-radius: 50%;6background-color: white;7top: calc(-50% - 0.5rem);8position: absolute;9box-shadow: 0 1px 6px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.15);10cursor: pointer;1112&:nth-of-type(2) {13 left: -2rem;14`}15`;1617// withComponent is from EmotionCSS to use a styled.div with a Framer Motion motion.div18const AnimatedKnob = Knob.withComponent(motion.div);1920const Track = styled(motion.div)`21 ${({ trackWidth, knobX, knobXSecond, trackWidthInPx }: any) => css`22 width: ${trackWidth}rem;23 height: 0.5rem;24 background-color: #3d5ef8;25 /* This gradient contains a calculation for the slider track. */26 background: linear-gradient(27 to right,28 #dae3f4 0%,29 #dae3f4 ${Number((100 * (knobX / trackWidthInPx)).toFixed(2))}%,30 #3d5ef8 ${Number(100 * (knobX / trackWidthInPx) + 8).toFixed(2)}%,31 #3d5ef8 ${Number((100 * (knobXSecond / trackWidthInPx)).toFixed(2)) -32 8 -33 0.01}%,34 #dae3f4 ${Number(100 * (knobXSecond / trackWidthInPx)).toFixed(2)}%35 );36 border-radius: 0.25rem;37 position: relative;38 margin: 1rem 0 2rem;39 `}40`;4142const Row = styled.div`43 display: flex;44 align-items: baseline;45 margin: 1rem 0 1.5rem;46 position: relative;47`;4849const AmountLabels = styled.div`50 font-size: 0.875rem;51 background-color: ${theme.colors.greyTags};52 border-radius: 0.5rem;53 padding: 0.5rem;54 display: inline-block;55 margin-bottom: 0.5rem;56`;
Using hooks
I used hooks to keep a state, update values and set references to certain elements/components. We also like to use TypeScript to keep things readable.
1// SliderParent.tsx2const SliderParentComponent = () => {3 const [sliderMin, setSliderMin] = useState(personalDetails.minBudget);4 const [sliderMax, setSliderMax] = useState(personalDetails.maxBudget);56 return (7 <Slider8 defaultMinBudget={personalDetails.minBudget}9 defaultMaxBudget={personalDetails.maxBudget}10 label={t('common:Core.whatIsYourMonthlyBudget')}11 max={4000}12 t={t}13 setSliderMin={setSliderMin}14 setSliderMax={setSliderMax}15 />16 );17};1819//Slider.tsx20// STYLING COMPONENTS HERE2122interface Props {23 max: number; //ex. 400024 defaultMinValue?: number; // If there is a value already, we use this as placeholder25 defaultMaxValue?: number;26 t: TFunction; // Our translation library for multi language (next18next)27 label?: string; //Text value of the label28 setSliderMin: (value: number) => void; // This is a state29 setSliderMax: (value: number) => void;30}3132export const Slider: React.FC<Props> = props => {33 const {34 label,35 max,36 t,37 setSliderMin,38 setSliderMax,39 defaultMinValue,40 defaultMaxValue,41 } = props;42 // We use trackLength to increase the length of the slider.43 const trackLength = 10;44 // `trackWidth` is the final width of the slider.45 const trackWidth = 1.5 * trackLength;46 // We use `rem` as our size values so we need to multiple the width by 16 (1rem = 16px)47 const trackWidthInPx = trackWidth * 16; //19248 // This is a scale to increase the size of the Knobs/Thumbs49 const knobSize = 2;50 const knobSizeInPx = knobSize * 16;51 // This is the amount of range we want to keep between two thumbs/knobs to avoid them stacking52 const knobSeparatorLength = knobSizeInPx * 2.25;5354 // max is a number value (ex. 4000)55 function getPixelValue(knob) {56 return (knob / max) * trackWidthInPx;57 }5859 // We calculate the value of the knob on the track. We like to increment in steps of 560 function getValueOfKnob(knob) {61 const value: number = parseInt(62 (max / (trackWidthInPx / knob)).toFixed(0),63 1064 );65 return Math.ceil(value / 5) * 5;66 }6768 // This is the first knobs value and position on the track.69 const [knobX, updateKnobX] = useState(70 defaultMinValue ? getPixelValue(defaultMinValue) : 071 );72 const [knobXSecond, updateKnobXSecond] = useState(73 defaultMaxValue ? getPixelValue(defaultMaxValue) : trackWidthInPx74 );75 // A constraintsRef to use set on the track and disallow the knobs to move further than the knob76 const constraintsRef = useRef(null);7778 // HTML/MARKUP HERE79};
Big thanks to @moniac for bugfixing ;)
Final words
That's it!
This component can for example allow a user to set their budget on an e-commerce website.
We gave the default values and final value state via useState hook as a prop, so we are able to use the value from the slider in it's parent.
Thanks for reading!
I hope someone somewhere learned something via this post! If you did, please consider sharing the article.
Other posts you might like
How I built the Level30Wizards page transition with Gatsby and Framer Motion
July 02, 2020Tech stack The Level30Wizards website is built with: Gatsby for templating, routing, etc. Framer…
Creating scroll snapping blocks with GSAP v3 animations
July 01, 2020Setting up some HTML So firstly I want to say something about using a lot of div elements. Stop…
Beginner guide to web animation to get started
June 30, 2020A Creative Front-End Developer or Motion Developer will make a UI or concept come to life on the web…